Introduction:
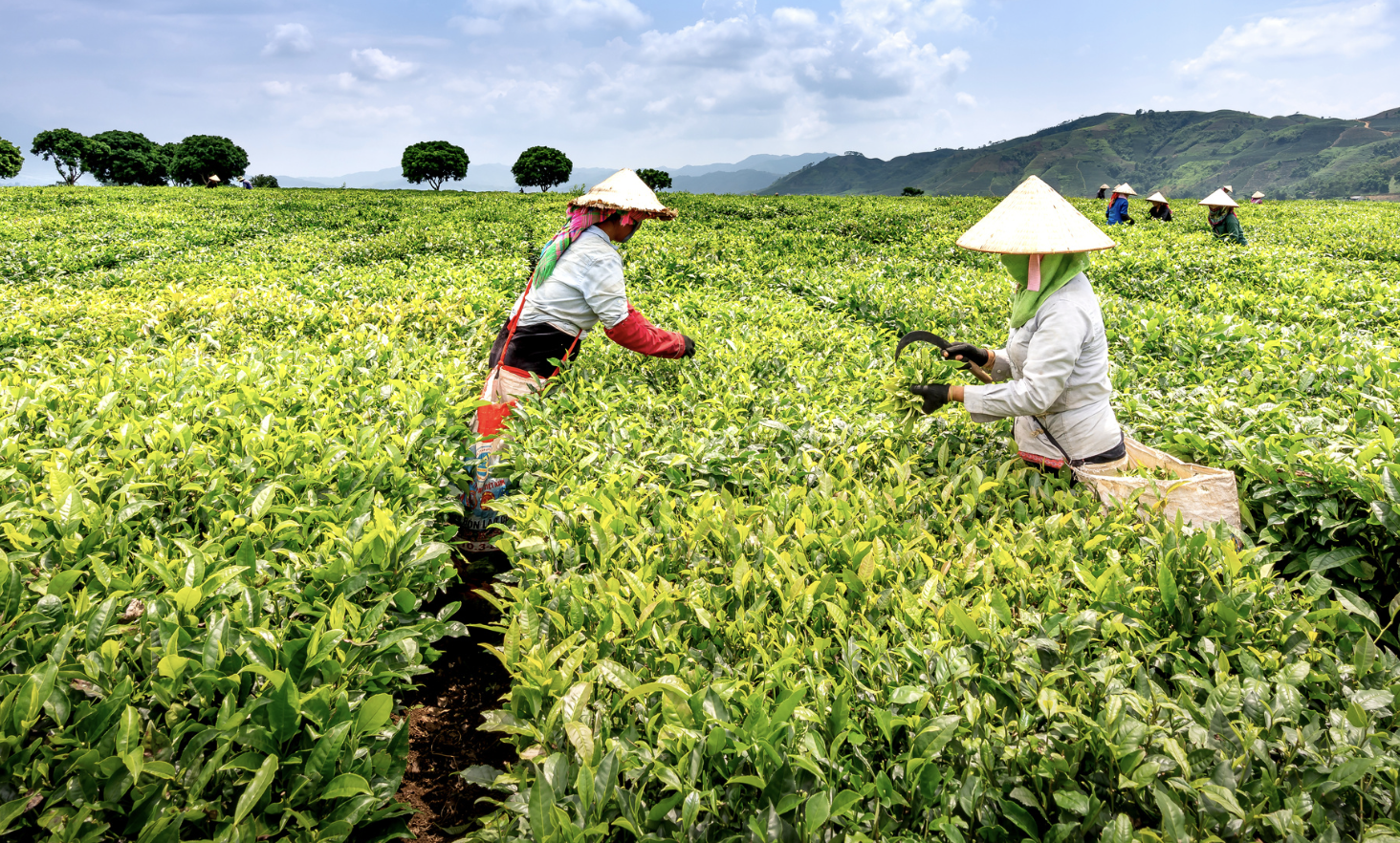
Africa, and specifically Nigeria, has the potential to achieve a sustainable system by embracing Distributed Renewable Energy (DRE) solutions. As highlighted in a recent report by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) and the Energy Commission of Nigeria, increasing investments in renewable energy can address energy poverty, combat climate change, enhance
food security, and reduce income inequality. This article explores the transformative power of DRE, focusing on the adoption of solar irrigation and biogas technologies, and their potential to revolutionize the agricultural sector.

Current Landscape.
Nigeria, with its rapidly growing population and energy poverty challenges, has recognized the significance of renewable energy in achieving energy security and economic growth. The Renewable Energy Roadmap for Nigeria recommends prioritizing the deployment of Distributed Renewable Energy (DRE) technologies such as solar photovoltaic power, hydropower, and biofuels. By investing $35 billion annually in renewable energy, Nigeria can generate 47% of its electricity from renewables by 2030 and 57% by 2050. These efforts would not only provide affordable and clean energy to consumers but also contribute to regional sustainable development, as demonstrated by the Rural Electrification Agency (REA) through the implementation of six 100kW mini-grid systems, benefiting communities such as Ijebu in Ogun State.
According to the Agency’s 2022 programmatic budgeting report, the six mini-grid projects were designed and installed to prioritize productive users, such as agro-processing businesses, homes, commercial users, and public spaces, with a focus on improving the lives of active farmers and enhancing productivity. The provision of uninterrupted power supply and clean, affordable water has had a significant impact on the lives of over 8,155 individuals and 5,000 active farmers. This has resulted in various positive outcomes, including:
The creation of over 60 direct and indirect jobs
Improved security
Increased productivity
Enhanced healthcare services
Decommissioning of more than 40 diesel and petrol generators
Reduction in carbon emissions
Furthermore, the report revealed that solar-powered irrigation pumps deployed across six geopolitical zones have positively affected more than 11,000 individuals and 6,000 farmers, including approximately 810 female farmers. This outcome has led to:
The lighting up of over 170 farms using Solar Street Lights (SSLs)
The training of over 3,000 farmers on pump maintenance and innovative irrigation techniques
Significant savings in maintenance and fuel expenses
Distributed Renewable Energy Solutions in the Agricultural Sector.
DRE solutions are crucial for addressing energy poverty in Sub-Saharan Africa, where nearly 700 million people lack access to electricity and approximately 1 billion people receive unreliable power. Africa is responsible for a small portion of global greenhouse gas emissions, but the agri-food system contributes approximately 59% of these emissions.
While progress has been made in the adoption of solar lanterns and home systems, the transition to productive uses of renewable energy has been limited. However, the potential market for productive-use DRE solutions in Sub-Saharan Africa is estimated to be over US$11 billion. This presents a significant opportunity to leverage solar energy and other renewables to drive sustainable development in the region.
DRE plays a pivotal role in enhancing food security by reducing losses in the agri-food chain and improving access to affordable energy. In developing countries, a significant portion of food is lost before reaching the market due to poor handling and inadequate storage facilities. Sustainable cold chains powered by renewable energy can help minimize these losses, ensuring food availability and reducing waste.
Additionally, DRE reduces energy costs for low-income households, empowering them to allocate resources to other essential needs and improve their overall quality of life. The systems also create local job opportunities, stimulating economic growth and reducing income inequality.
Integrating DRE in the agricultural sector offers multiple benefits, as around 38% of the energy utilized within the agri-food system is lost through food losses along the value chain. Agri-food systems rely on fossil fuels, which account for a significant portion of energy consumption.
By adopting DRE systems such as solar irrigation and biogas, farmers can:
Reduce reliance on costly and polluting fossil fuels
Increase agricultural productivity
Mitigate the impact of climate change
Solar Irrigation & Biogas: Key Agricultural Innovations
Solar irrigation systems powered by solar energy enable farmers to:
Biogas systems, on the other hand, convert organic waste into clean energy and nutrient-rich biofertilizers, which:
Improve soil fertility
Enhance crop quality
Enhancing Market Access & Economic Growth
Solar irrigation and biogas systems provide farmers with the tools to improve market access:
By mitigating the limitations of rainfed agriculture, farmers can plan their production schedules more efficiently, aligning with market demand throughout the year.
Additionally, biogas systems not only provide renewable energy for cooking and machinery, but they also enable value addition to agricultural products. Processed goods and organic produce fetch higher prices, opening up new market opportunities.
....
Key Statistics.
38% – Around 38% of the energy utilized within the agri-food system is lost through food losses along the value chain.
59% – Africa is responsible for a significant portion of global greenhouse gas emissions, with the agri-food system contributing approximately 59% of these emissions.
57% by 2050 – By investing $35 billion annually in renewable energy, Nigeria can generate:
....
References.
IRENA (2023). Renewable Energy Roadmap: Nigeria. International Renewable Energy Agency, Abu Dhabi.
Using Distributed Renewable Energy to Create a Just Energy Transition. ESI-Africa, June 15, 2022.
Available at
Renewable Energy Sparks Africa’s Sustainable Agrarian Transformation (Fact Sheet). Power For All, May 2023.
Available at
Rea’s Strategic Interventions: Adopting a Programmatic Approach to Deliver Capital Projects. Rural Electrification Agency, March 27, 2023.
Available at



